Factors of production are the resources used to produce goods and services, and are the building blocks of an economy. Economists categorize these resources into four types:
The four factors of production
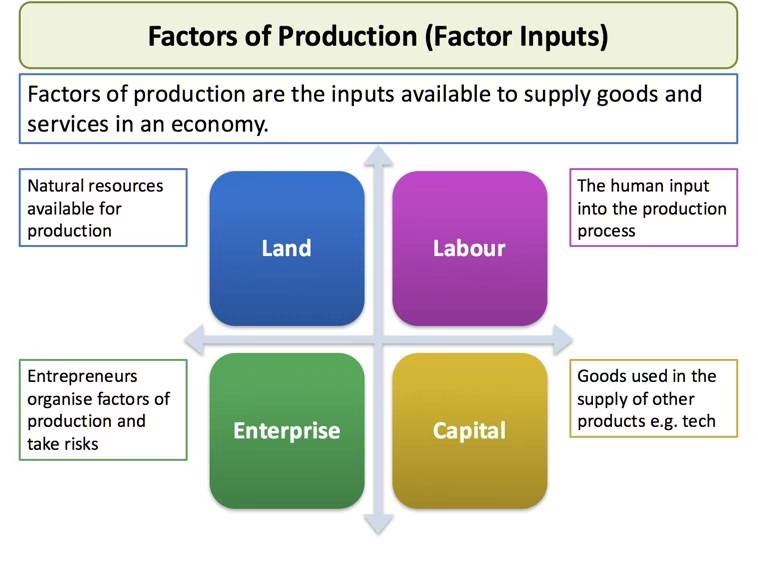
Land
By land in economics we mean all that is given to us free by nature, on or below or above the surface of the earth. On the surface it includes, the soil, water, forests etc. below the surface it includes mineral deposits, water streams, petroleum etc., and above the surface it includes the sun, light, wind etc.
As the land(natural resource) became scarce, sale and purchase of land started. Those who owned land started charging price for the use of land. Such a payment to the land owner/landlord is termed as rent.
Labour
Labour includes all physical and mental efforts of human beings used for production of goods and services. These physical and mental efforts are inseparable. A worker requires both. Some of the jobs requires more of physical labour than mental labour and some jobs require more mental labour than physical labour.
The remuneration paid to the workers is popularly termed as wages and salaries. In national income accounting, it is termed as compensation of employees(wage).
Capital
Capital includes all the man made resources used for producing goods and services like structures on land(buildings), machines, equipment’s, vehicles, stock of materials etc.
The payment made to the owner of capital for the use of capital is termed as interest.
Fixed Capital Vs Working Capital
Fixed capital refers to any kind of physical assets like buildings, machinery it stays in business for a long time ans experience depreciation over the period of its usage.
Working capital refers to investments made on raw materials, inventory etc,. normally they are meant to be consumed in a year or in single product cycle.
Human Capital
The term human capital refers to the economicvalue of a worker’s experience and skills. Human capital includes assets like education, training, intelligence, skills, health, and other things employers value.
Physical Capital
Physical capital is the physical property or tangible assets that the company owns. This would include the buildings or other real estate the company owns, machinery, tools, and equipment. These items can be sold directly, often depreciate over time or with use, and will be listed in financial statements as assets.
Intellectual Capital
For most companies, intellectual capital comprises the larger share of value – perhaps up to 80% of valuation is dependent on things that cannot be held or sold directly. Intellectual capital is comprised of things the company’s management or employees contribute to its overall profitability like:
- Knowledge
- Talent
- Skills
- Abilities
Capital Output Ratio
- Capital Output Ratio (COR) is the amount of capital required to produce one unit of output.
- It is the relationship between the level of investment made in the economy and the consequent increase in Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- It also expresses the relationship between the value of capital invested and the value of output.
- Higher capital output ration indicates, one is using more capital to produce a given output, higher is the COR, lower is the efficiency of capital.
- Economies with higher COR tend to report low growth due to inefficient utilization of the scarce capital.
Example of COR:
- For example, investment in an economy is 32% of GDP, and the economic growth corresponding to this level of investment is 8%. Here, it means that an investment of Rs. 32 produces an output of Rs. 8. Therefore, the COR is 32/8 i.e., 4.
- In other words, to produce one unit of output, 4 units of capital are needed.
Incremental Capital Output Ratio(ICOR)
Is a metric that assesses the marginal(additional) amount of investment capital necessary for a country or other entity to generate the next unit of production.
It’s the additional units of capital investment needed to produce an additional unit of output.
Higher the ICOR, lesser is the efficiency of capital.
Entrepreneurship
It refers to the initiative taken by a person or a group of persons in starting and organising a business. Unless somebody takes this initiative, no business can be started. The one who takes this initiative is termed as entrepreneur.
The income accruing to the entrepreneur is termed as profit.
Thus compensation of employees(wages), rent, interest and profit are factor incomes of the factor owners.
